Study Area
GE lab has 4 research fields as (R1) Sustainable Use of Ecosystem Services, (R2) Carbon Management for Mitigation and Adaptation against Climate Change, (R3) Biodiversity Conservation Technology Development, and (R4) Natural Symbiotic System Design. You can see the research samples of our study field below.
For more details, see also Graduate Thesis page and Publications.
Research target_01: Sustainable Use of Ecosystem Services
R1-1: Service Linkage between Natural and Social ecosystems
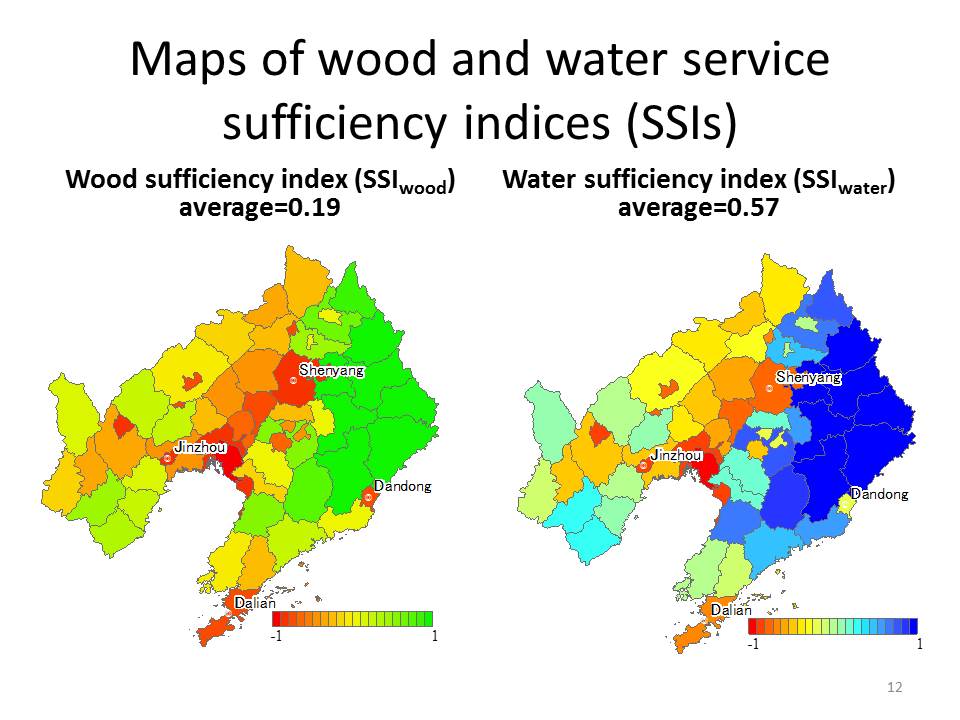
生態系から人間社会にもたらされる資源・環境調節機能・文化などの様々な便益を、生態系サービスと呼びます。持続可能な生態系サービス利用は、自然共生社会の基本的要件です。生態系サービスの需要・供給構造を分析し、持続可能な利用方法をデザインするため、自然生態系と社会生態系のプロセスを統合するサービスリンケージモデルを開発しています。ケーススタディとして、中国遼寧省における木質資源・水資源供給サービスのバランスを示します。
A variety of benefits provided to human society by ecosystems including resources, environmental conditioning and cultural motifes is calld "ecosystem service". Sustainable use of ecosystem services is a fundamental condition for the nature sound society. We are developing a service linkage model that aggregate processes of natural and social ecosystems aiming to analize demand-supply balance of, and to design sustainable use of ecosystem services. Wood and water provision service sufficiency is shown from a case study in Liaoning, China.
R1-2: Multiple benefits design of biomass production and use
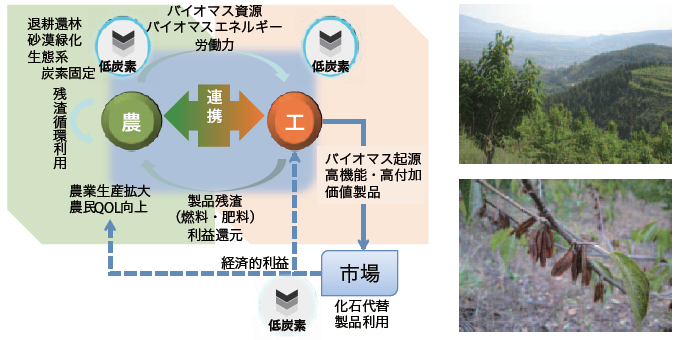
アジア新興国では急速な経済成長の陰で,都市と農村の格差や環境悪化の問題が起きています。農村部の自然資本を利用したバイオマス産業は,環境改善と農村 の社会・経済的発展において,様々な便益が期待できます。中国河南省の黄土高原地域では特産の杜仲の木を栽培し,健康食品,天然ゴム,BDF などを製造するパイロット事業が始まりました。この事業をケースタディとし,生態系炭素固定や土壌保全などの環境保全効果,バイオマス高度利用による低炭 素化効果,収益や農民生活向上などの社会経済的効果を評価する研究をおこなっています。
Issues of domestic disparities and environmental degradation arose behind a rapid economic growth in Asian developing coutries. Biomass industries that utilize natural capital are expected to provide multiple benefits of environmental improvement and socio-economic development in rural regions. A pilot enterprise that plants Eucommia ulmoides trees and produce health keeping foods, natural rubber, BDF etc. was established in Henan Province, China. We are conducting a case study to evaluate its various effects in ecosystem carbon sequestration, soil protection, carbon emission reduction by substituting fossile oriented energy and materials, economic profits and farmers' welfare.
R1-3: Development of Evaluation System of Ecosystem Servuces Use in Social Activities
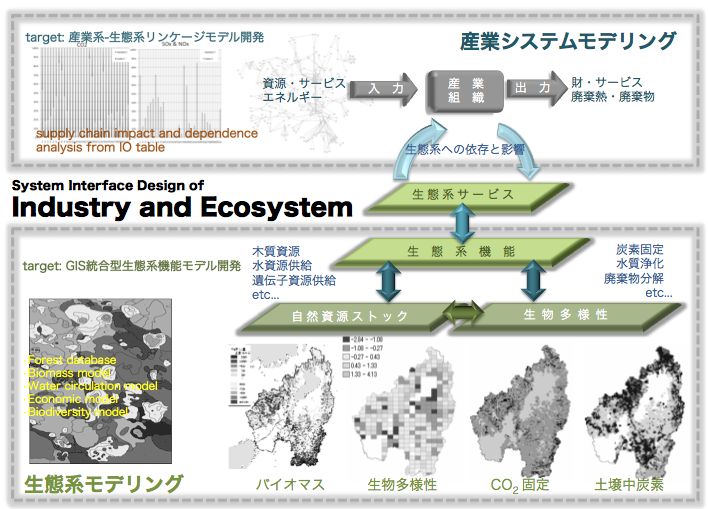
産業システムは生態系の生み出す多種多様な生態系サービスに依存するとともに,産業活動に伴う環境負荷が反作用となって活動に影響を及ぼすというフィード バックシステムを形成しています。これらのシステム全体を持続可能なものとするべく,生態系と産業系に存在している様々なモジュールの分析と,それらのモ ジュールを共生システムとして統合するための持続可能なインターフェイスのデザインをする研究を実行しています。
Industrial systems strongly depend on various and huge amount of services provided by ecosystems and environmental impacts posed by industrial activities affect ecosystems’ state and biodiversity. From this view points, we are analyzing various modules in human society ecosystems like industries, economics and cities sphere and trying to develop a system to evaluate "Ecosystem Services Use" in Human activities.
R1-4: River Basin Ecosystem Management
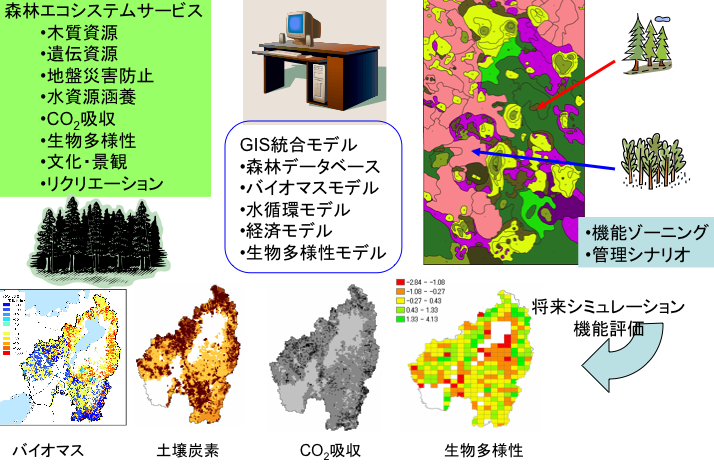
森林には多様な公益的機能があり、それらの期待は大きく,公益的機能保持には森林ゾーニングと適切な森林管理が重要です。ところがこれまでの森林管理は、森林生態系サービスの供給側条件のみを考慮しており、受容側の条件は考慮されてにくいことから,地域人口の動態によって森林管理可能面積が変化し,生態系サービスの受容が変化することが考えられます.そこで本研究では,人口動態のシナリオアプローチを用いて森林管理による生態系サービスの変化を予測・評価するフレームワークを開発しました.
R1-5: Development of Decision Suppoert System for Optimal Biomass Use
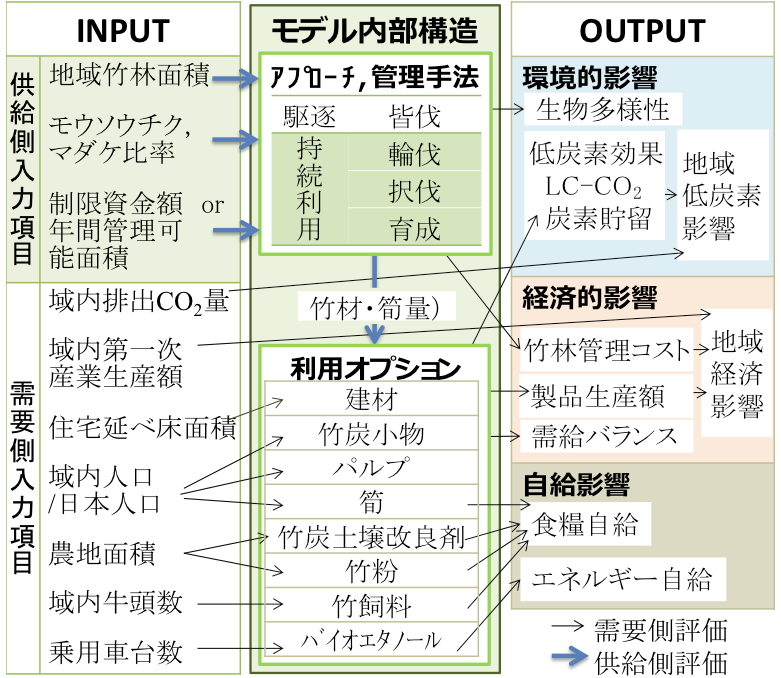
現在竹林の放棄が進み,様々な問題が生じています.そこで本研究は竹林の適正な管理の支援を目的に,竹林へのアプローチと管理手法を示し,竹材資源量推計サブモデルと資源特性に応じた利用オプションの環境・経済評価モデルを開発しました.具体的には,モデルの入力は地域の竹林面積と人口等の地域情報,出力は低炭素効果や生物多様性影響,地域内食糧自給ポテンシャル,竹林管理コスト等で,モデル内部構造は竹林管理に関するアプローチ,管理手法,利用オプションをもった環境経済統合評価モデルです.利用者は農地面積や制限資金額等の入力により,地域特性に応じた竹林管理の評価が可能となります.
Recently Bamboo forests have been abandoned and it causes many environmental problems. Under this background, a tool that can evaluate environmental and economic impact of bomboo forests management was developed in this study. This model structure includes, strategies, banboo resource use options and management approaches and sub model to evaluate social-economic and environmental aspects. Specifically model inputs are the area of banboo and socio-economic characteristics of the target region and main model outputs are low-carbon effects and impacts to ecosystems, self sufficiency in the target region. Then this model was applied to Kobe city and Awaji resion, the former is the central urban city and the later is the rural area of Hyogo prefecture in Japan. This result implicates some effective bamboo management ways reflecting the characteristics of these two region. It is expected that this decision supporting model of bamboo forests will supports to plan the bamboo forest management under each regional environmental and socio-economic contexts.
R1-6: Assessing Demand and Sullpy Balance of Consumer Sectors on Ecosystem Service on a Regional Scale
都市化の進展とともに都市の生物多様性の重要性が認知され,都市活動と生態系との関連性から都市計画を見直すことの必要性が指摘されています.そこで本研究は森林に関する生態系サービスへの依存度を生態系面積単位で評価するエコロジカル・フットプリントを基にしたフレームワーク(Ecosystem Service Use:ESU)を用いて,大阪府の市区町村レベルで都市活動の主な活動形態である民生業務部門活動の生態系サービス依存度を評価・分析しました.その結果,対象とした9業種によってFESU(Forest Ecosystem Service Use)の合計値は大きく異なりますが,ほぼ全ての業種で森林生態系のCO2吸収サービスへの依存度は高く,市区町村別での生態系サービス依存度の分析では大阪市中央区と北区の2区の生態系サービス依存度が非常に大きい値を示しています.各市区町村の民生業務部門の業種構成割合,民生業務部門の従業員数あたりのFESU,森林生態系サービスへの域外依存度を変数としてクラスタ分類を行うことで,それぞれ特徴を持つ5つの地域に分類することが出来ます.
Recent rapid urbanization is globally placing strain on ecosystems and with it a growing awareness of the issues of urban biodiversity conservation and sustainable use of ecosystem services. The purpose of this study is to clarify the relevance between urban activities and ecosystems. The research approach applied evaluates the degree of dependence of consumer sectors on forest ecosystem services at municipalities in Osaka Prefecture. This evaluation was followed with hierarchical clustering using variables representing the characteristics of consumer sectors of each municipality. It was found that urban activities in Osaka Prefecture primarily depend on the service of CO2 absorption. The results also show what activities are most likely to create a demand for ecosystem services. From the hierarchical clustering, the municipalities can be divided into five separate clusters of varying characteristics. Furthermore, it was understood that there is an overuse, or imbalance, in ecosystem service use at almost every municipality in Osaka. It is believed that these results can contribute to the development of indices for biodiversity conservation and sustainable use of ecosystem services in urban ecosystems. Future research includes increased coverage of ecosystem services, and expansion to examine other regions for a more precise and holistic grasp of dependences on ecosystem services.
Research target_02: Carbon Management for Mitigation and Adaptation against Climate Change
R2-1: Development of high spatial- and temporal- resolution anthropogenic CO2 inventory in City Scale
温室効果ガスの排出量を削減するために,定量化を通じた削減活動の明示化が必要であり,それには排出の活動単位毎の推計と実測データを用いた排出量の検証が必要です.都市域では温室効果ガスの排出活動が細かな空間スケールで複雑に行われており,行政単位で推計した既存のインベントリは時空間的な不確実性を持ちます.そこで本研究は,大阪府域から人為起源により排出されるCO2の時空間分布を詳細に推定する手法を提案し,他のインベントリや実測データとの比較により評価を行いました.
In recent years, methods to estimate greenhouse gas emission sources and to verify emission reduction by using observed data and inversion techniques are proposed. For use in them, an emission inventory of high spatial and temporal resolution is needed. In this study, We classified the anthropogenic CO2 sources into point sources (thermal power plants, etc.), a line source (road transportation) and distributed sources (residence, etc.), and estimated annual emission using quantitative activities and emission factors in each sector. Then We identified the location of emission sources using aerial photographs, road maps, and population density, and estimated time series using the time courses of activities. As a result, the spatial resolution of distributed source was improved and the temporal resolution to monthly to daily to hourly.
R2-2: Development of high spatial- and temporal- resolution anthropogenic CO2 inventory in City Scale
気候変動が与える影響を最小化するためには,それぞれの地域の特徴を考慮した詳細な気候変動の適応策の検討が必要であり,地域スケールでの様々な影響を評価することが求められています.そのため,IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) が第5次評価報告書のために開発したRCPシナリオ (Representative Concentration Pathways) を利用した影響評価の高解像度化が期待されており,代表的な先行研究では気候変動に伴うブナなどの潜在生息域の変化が予測されていますが,プロセスベースの植生遷移や種子散布,人為的攪乱が表現されることが期待されています.そこで本研究では,RCP8.5シナリオと森林景観シミュレーションモデルを用いて,森林施業に起因する植生遷移を予測することで,地域スケールのバイオマス量や樹種構成への影響を評価しました.
Climate change impacts on forest composition and the distribution of tree species. To develop a climate-change adaptation plans, regional impact assessment on the forest under climate change is required. In this study, We simulated forest landscape dynamics in Ishikawa Prefecture using the forest landscape simulation model, LANDIS-II. The result shows that the rate of change of tree species composition differed between the RCP8.5 scenario and current climate scenario after a disturbance, natural regeneration, by regional scale. As the result of RCP8.5 scenarios, climate change effects on forest composition depending on the region.
R2-3: Ecosystem Succession and Carbon Circulation Analysis after Forest Management in East Siberia
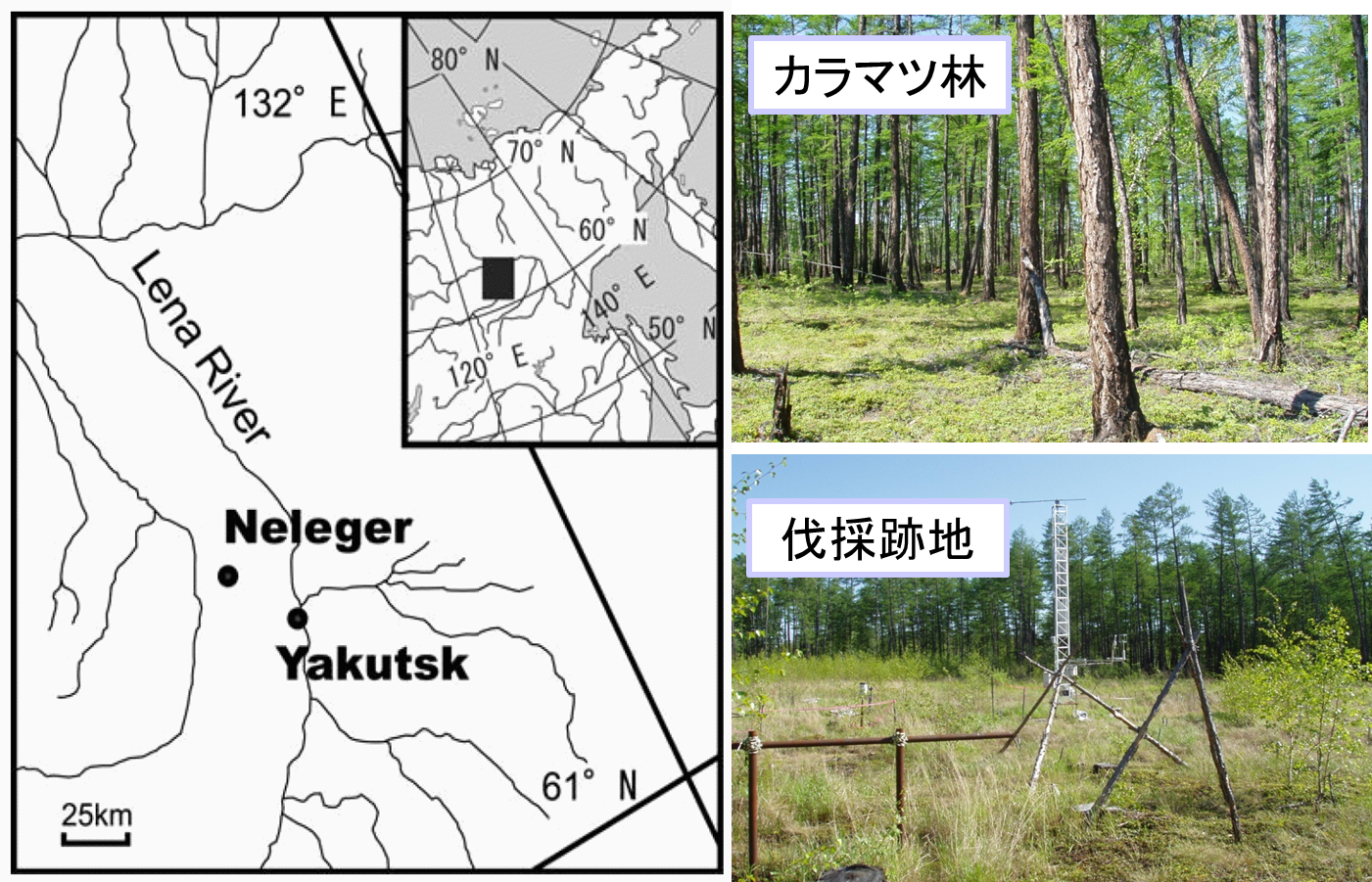
東シベリアに広がるカラマツ林はその広大な面積から炭素蓄積量も多く、地球炭素循環において重要です.しかし東シベリアでは違法な伐採や森林火災による森林生態系炭素循環への影響が懸念されています.森林撹乱が森林生態系炭素循環に与える影響のメカニズムは非常に複雑で,また伐採後におけるCO2フラックスの長期観測における報告が少ないことからもまだ解明には至っていません.そこで本研究では、東シベリアのカラマツ林およびそれと同一林分の一部であった伐採跡地において植生調査およびCO2フラックスの長期観測を行い,伐採後7年間の植生遷移と生態系炭素収支について解析しました.
Forest disturbances have often occurred in eastern Siberia and become concerned about their impact on the carbon cycle of forest ecosystems. However the mechanism of the disturbances on the carbon cycle of the forest ecosystems is complicated and still uncertain due to little information, especially on the CO2 flux after clear-cutting. Therefore, in order to understand the influence of clear-cutting, the interannual surveys of vegetation at the clear-cut site and long-term observations of CO2 fluxes at both the clear-cut and forest sites were conducted at a larch forest in eastern Siberia. The vegetation composition at the clear-cut site had drastically changed, in which gramineous species invaded and influentially pervaded. The aboveground biomass rapidly decreased soon after harvesting, it however gradually increased due to the vegetation recovery. Total net ecosystem exchange for the growing season at the clear-cut site was gradually decreased, resulting from 398 g C m-2 in one year after clear-cutting to 82 g C m-2 in seven years after that. The clear-cut site, however, was still a carbon source for seven years after clear-cutting.
R2-4: Meso Scale Mapping of CO2 source and Sink
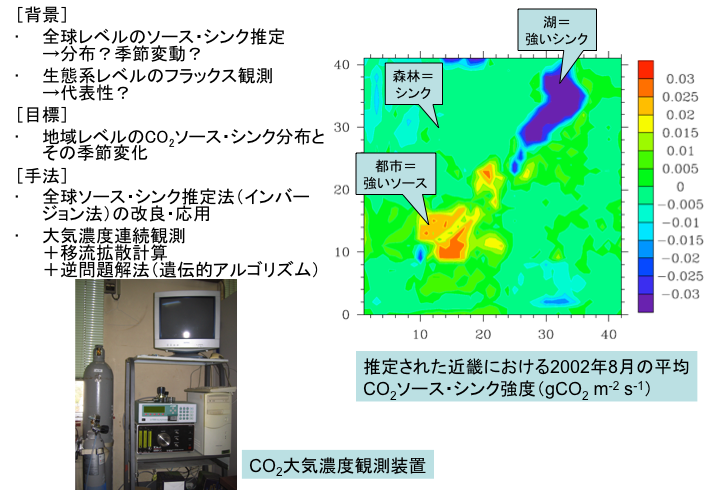
温室効果ガスの排出は気候変動に対して大きな影響を与えるため,温室効果ガスの排出量をモニタリングすることは,炭素管理上重要な役割を持ちます.特に,温室効果ガスのインベントリと大気中の温室効果ガス濃度のシミュレーションを連携させて,国別・地域別など重層的な時空間スケールで炭素排出をトラッキングできるシステムの開発が求められています.そこで本研究では,二酸化炭素のソース・シンクを高解像度に把握するための簡易推計手法を開発しました.
Global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions need to be reduced to stabilize atmospheric concentration. Global compliance of emission reduction such as the Kyoto Protocol has been monitored using GHG inventories reported annually by nations, however GHG inventories do not allow for emission monitoring beyond the national spatial scale and annual time scale. Moving towards future systems to address the emission reduction such as emission trading and carbon footprint, an independent tool to quantify regional and local sources and sinks that can be used for emission management by local governments and commercial companies is likely to be necessary. Source and sink estimation by the inversion of atmospheric concentration also has technical difficulties at such spatiotemporal scales. In this study, a simplified inverse method for estimating regional CO2 sources and sinks was developed and requirements for obtaining better regional estimates were investigated. Subsequently, a high-resolution fossil fuel CO2 inventory and high-resolution transport modeling system were developed and their performance was evaluated.
Research target_03: Biodiversity Conservation
R3-1: Monitoring Technology Development of Wild Animals
コウモリ類は豊富な種の多様性と広大な分布域を持つと同時に,種子分散や送粉,農業害虫の捕食など,生態系の中においても重要な役割を担っています.その一方で,環境の変化には非常に敏感であるため,環境モニタリングの指標生物として非常に有効であるとして近年注目を集めている.モニタリングの際には,飛翔時や餌の探索時に発するエコーロケーションコールと呼ばれる超音波を解析することで種の推定をする試みが進められており,本研究では,機械学習を用いることで高精度な種の識別が可能な識別器を構築しました.
Recently acoustic monitoring by echolocation call of bats attracts attention because it will support to evaluate environmental conditions. However ultrasound call of bats has a large variety depending on the species’ characteristics, activities and surrounding environments. Therefore it is needed to develop classifier which can identify bat species by various echolocation calls precisely. In this study, we developed a bat species classifier based on Machine learning algorithms and applied it to an acoustic monitoring. We applied the classifier to a site in Osaka, Japan and we estimated the existence of bats. Based on the result, we discussed the improvement of classifier and applicability to the real field.
R3-2: Simulation of Expansion of Invasive Species
セアカゴケグモ (Latrodectus hasseltii) は日本では1995年にはじめて発見され,2005年に特定外来生物に指定された.また,原産国であるオーストラリアで神経毒により死者を出したこともあり,その死亡率は約5 %でといわれています.セアカゴケグモは自然拡散に加え自動車などによる人為的移動を行うため分布域が急速に広がっているので,近年増加している咬傷被害件数を減らすよう管理する必要があるため,本研究では自然拡散と人為的移動を同時に考慮したセアカゴケグモの分布拡大予測を行いました.
An alien species, red back spider Latrodectus hasseltii is toxic and the monitoring and prediction of its occupancy area expansion are required to reduce accidents. In this study, we predicted the occupancy area expansion by using a bayesian-based metapopulation model integrating random walk and anthropogenic transportation. The random walk migration probability was estimated by the function of annual migration distance. The anthropogenic migration probability was determined by geographic attributes regarding transportation facilities and traffic intensities. I validated the predicted migration probability by comparison to the distribution map until 2016, and it is showed that the migration probability including anthropogenic transportation was more successfully simulated than the probability including only random walk.
R3-3: Evaluation of Social Responsibility for Biodiversity Conservation
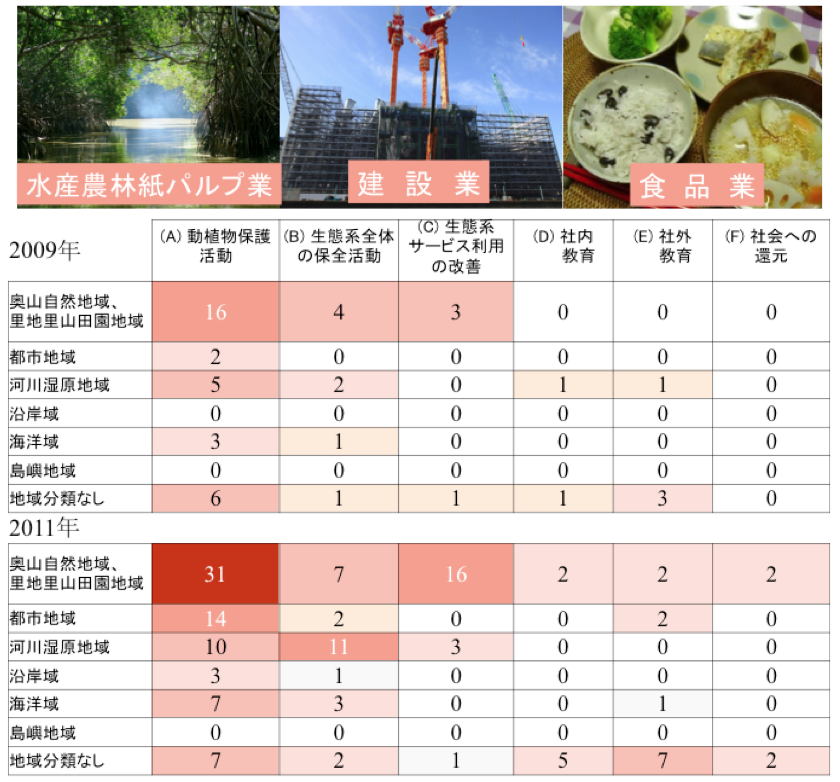
現在,地球規模で生物多様性が喪失されつつあり,生物多様性損失速度を減少させることや,これらから受ける生態系サービスの公正・衡平な配当を目指すための国際会議である生物多様性条約CBD-COP10が2010年に名古屋で行われ, 産業セクターが生物多様性保全の取り組みを強化していることが予想されます.そこで本研究では,水産農林・紙パルプ業,建設業,食品業を対象として,生物多様性条約CBD-COP10の前後である2009年と2011年の2時点で,企業の生物多様性保全の活動の傾向をCSR報告書から分析し,取り組みの進展度合いの評価や具体的な生物多様性保全活動事例の傾向を類型化しました.生物多様性保全活動を報告する企業が20%から60%,生物多様性保全活動の事例数も55から143に増加したことが明らかになり,また保全活動の内容がより各業種の事業の持続可能性に関連するような内容に変化している傾向を明らかになりました.
Recently, biodiversity has shown a decreasing trend on a global scale. In 2010, CBD-DOP10 was held in Nagoya in order to find ways to slow down this trend and promote equal distribution of profits from ecosystem services. Additionally, 2010 was declared Year of Biodiversity in order to increase biodiversity awareness within the society and industries. As a result, economic sectors efforts in biodiversity conservation were predicted to have increased since 2010. Therefore, this research studied trends in conservation efforts and concrete measures in biodiversity conservation actions between the years 2009 and 2011 for companies in agriculture, forestry and fisheries, pulp production, food and construction economic sectors. The differences were studied using CSR and other sustainability reports. The results show an increase from 20% to 60% in reported conservation actions and an increase from 55 to 143 in the number of concrete conservation measures. In addition, the contents of the reports studied showed a general trend towards sustainability across the sectors. Further research needs include examining of the relationships of economic sectors and ecosystems, and based on synergic relationship examples, ultimately the construction of a conservation best-practice database.
R3-4: Simulation of changing forest structure and landscape diversity by forest management and the abandonment of cultivation using LANDIS-II model
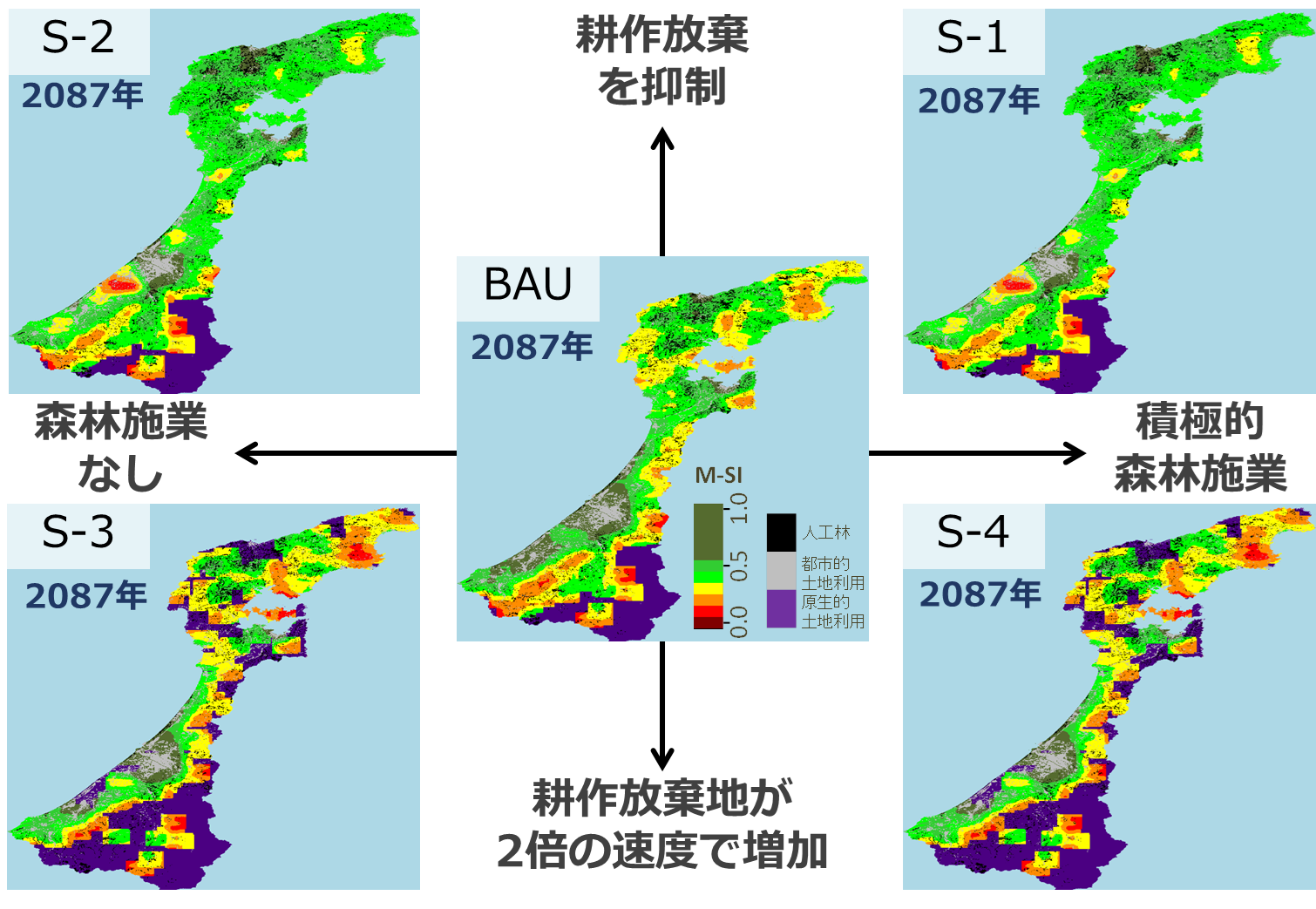
現在,SATOYAMAイニシアティブでは日本の里山利用をモデルとした自然共生社会が推進され,里地里山での生物多様性や生態系サービスの定量評価や持続可能な利用のための管理モデルの確立が求められています.この背景から,里地里山利用の適切性を科学的に評価するための手法の開発が進められており,森林や農地の管理シナリオ間の持続可能性の比較や気候変動などの駆動力の変化を考慮した動的な評価モデルへの拡張が求められる.そこで本研究では森林景観モデルのLANDIS-IIによって里地里山を含む地域の植生の遷移を再現することで,動的かつ空間的にシナリオ分析を行いました.
The sustainable management of Satoyama landscape is a major to realize a society in harmony with nature. In order to support the sustainable management, quantitative assessment and projection method of biodiversity and ecosystem services in Satoyama landscape is needed. In this study, Our team conducted a scenario analysis of managing forest ecosystems and abandoned agricultural land using LANDIS-II in Ishikawa Prefecture. The result shows that abandoned agricultural land succeeded to secondary forest and biomass carbon was accumulated in it. As the result in the cultivation abandonment scenario, landscape became more homogeneous and this decreased M-SI.
Research target_04: Natural Symbiotic System Design
R4-1: Development and Application of a Multi-Objective Optimization Tool for Renewable Energy Mix in Municipalities
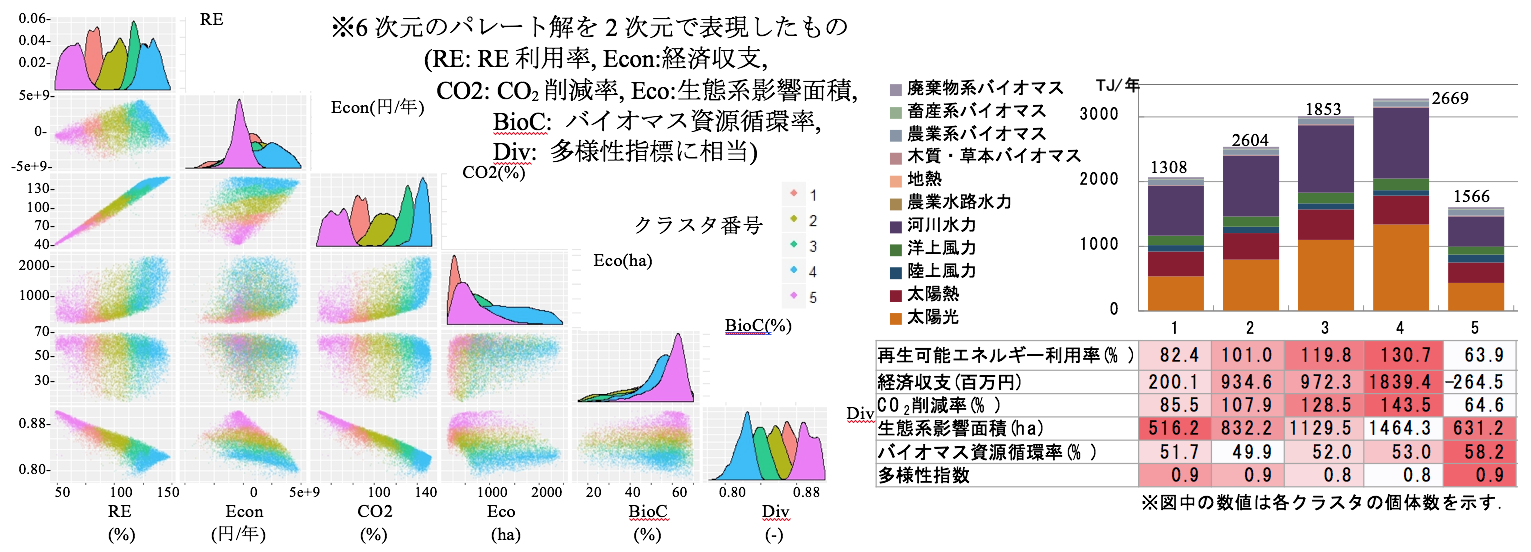
小規模分散型の再生可能エネルギーの普及促進のためには,市区町村等の地域コミュニティが主体となり,安定性や経済性等の条件を満たし,かつ環境影響の少ない地域適合型の再生可能エネルギーミックスを検討する必要があり,バイオマスの循環や地域の生態系への影響も考慮されなければなりません.本研究では,多面的な環境指標を加えた,再生可能エネルギーミックスの地域別最適化計算及び評価ツールを開発しました.区町村別の再生可能エネルギー供給ポテンシャルとエネルギー需要のデータベースと,再生可能エネルギーの組み合わせを評価する 6 指標(再生可能エネルギー利用率,経済収支,風力発電導入率,CO2削減率,バイオマス資源循環率,生態系影響面積)を作成し,複数のシナリオについて最適化計算を行った結果,シナリオごとに異なる再生可能エネルギーの組み合わせ最適解を導出でき,様々な再生可能エネルギーミックスの組み合わせ最適解を市区町村レベルで導くツールを開発しました.
To introduce the renewable energy in regional communities, it is necessary to select a sustainable energy mix on the basis of evaluation from multiple viewpoints including complex environmental impacts. The purpose of this study is to develop a tool for multi-objective optimization and evaluation of renewable energy composition in municipalities considering multiple environmental criteria. This tool was developed by creating a database of energy demand and renewable energy supply potential of all municipalities in Japan and designing six objective functions as evaluators. NSGA-Ⅱ, a kind of genetic algorithms was applied as a method to solve multi-objective optimization. A case study for a municipality showed that the developed tool successfully calculated pareto solutions having trade-off and one best solution could be selected from the pareto solutions.
R4-2: Accounting Technology Development of Inclusive Wealth
United Nations University International Human Dimensions Programme on Global Environmental ChangeとUnited Nations Environment Programmが発表した包括的な豊かさの指標(Inclusive Wealth Index, IWI)では,生産資本や人的資本に加え自然資本や社会資本の変化を評価するため,国家を経済・社会的持続可能性を長期的に検討することができます.特に日本の農村地域では,市場を介さない食料の自家生産やおすそわけが頻繁に行われており,これらの活動は人々の食生活を量的にも質的にも豊かにしている.それらを定量的に評価することで,経済指標だけでは測ることができない包括的な地域の豊かさを測ることが期待できます.本研究では自然資源が豊富な八丈島を対象にヒアリング調査とアンケート調査を実施することで,食料の自家生産やおすそわけといった社会的ネットワークによる食料の流通量を対象に既存の統計情報と比較可能なアカウンティング手法を開発しました.
In rural areas of Japan, agricultural products are produced at home garden frequently and distributed with non-market-based transfer. These activities enrich people 's eating habits both quantitatively and qualitatively, but they have not been quantitatively clarified. In addition, in Hachijo island with abundant natural resources, there are many special food products, which are promoted to consume them in the island. Therefore, in this study, by conducting a questionnaire to the islander in Hachijo island, We clarified the consumption behavior and substance flow over the dietary habit of Hachijo islander, and examined how the social networks such as home production of foods, and local production for local consumption plays the role in economy and natural capital of a community.
R4-3: Knowledge Management for Establishing Natural Symbiotic Society
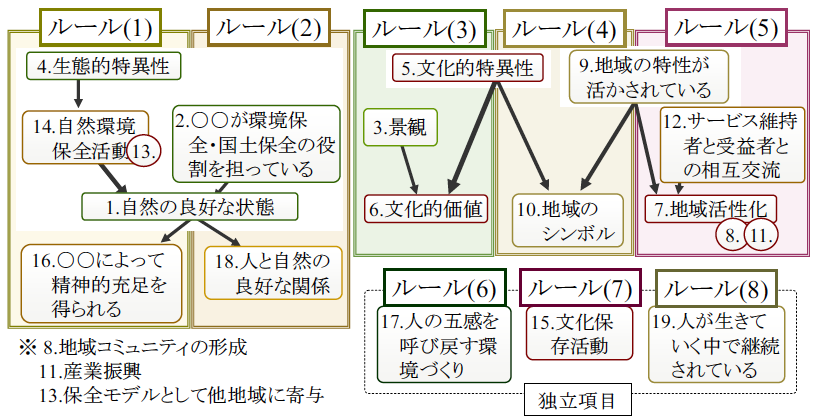
人と自然の良い関わりの再構築のため,日本での持続可能な人と自然の関わりを評価するためのデザインルールの構築を目的とした研究です.日本の価値観を反映した地域財の評価に「百選」がありますが,自然との関わりに関する百選には,持続システムを構築するための人と自然の共生に関する知恵があると考えられます.そこで,自然財を対象とした13の百選で採用されている54の選考基準を参考にして構築した要素を知識構造化し,デザインルールの構築を行いました.結果,自然保全のための因果関係を発見,8つのデザインルールを得て,ここから日本では自然を自分達の生活との関わりの中で意味づける傾向,文化性を重んじる傾向があるということが示されました.